Sterilization means the process of reducing the microbial population to the acceptable levels and maintain the sterility of the drugs or medical devices.
As appropriate, there are different types of sterilization techniques used to make contamination-free product contact parts. For example, Steam Sterilization, Dry Heat Sterilization, Ethylene Oxide Sterilization, etc.
Out of them, the F0 value (read as F Zero) is designed for moist heat sterilization (or steam sterilization).
In this article, you’ll learn:
- Mechanism of steam sterilization
- Background to and Calculation of the F0 value
- Understanding the meaning of the resulted F0 value
- Practical examples of the F0 value
So if you want to excel in the F0 calculations, this guide is for you.
First thing first, let us see the fundamentals of moist heat kinetics through mathematical and biological angles. Later, we’ll see how it connects with the F0 value concept.
Table of Content
Steam Sterilization Kinetics (Math vs. Bio)
Assume a microbial species that has contaminated the system, is in contact with saturated steam at a constant temperature.
Mathematically, sterilization develops as a first-order chemical reaction (more specifically, a biochemical reaction).
The rate of the reaction then becomes:

Where,
N – Number of microbes present in the system
t – exposure time to the microbes with steam
K – the rate of reaction’s constant (species dependent)
Re-arranging to integrate,

Now integrating,

Converting and simplifying the logarithmic value to exponential,

where,
N0 – no. of microbes initially
t – steam exposure time (sterilization hold time)
N – no. of microbes at the end of sterilization hold
k – the rate of reaction constant (microbes dependent); now this k = K / 2.303. Here, K is called the Death Rate constant.
The equation (1) hence shows that no. of microbes decreases exponentially with increasing sterilization hold time. Also, the time required to decrease the microbial amount to a pre-defined
value depends on its initial number.
What is D-Value (Decimal Decay Time)?
D-value is the time (t) required at a specified temperature (T) to reduce the microbial population from 100% to 10% (i.e. 90% or 1 log reduction).
Definition of D-value
Mathematically, the D-value is the reciprocal of rate of reaction constant (k) and therefore;
K = t -1
By putting this value in earlier equation (1) we get,
N = 0.1*(N0)
The D-value plays an important role in determining hold time for the system under the sterilization.
More commonly, D-value is considered as “1” if there is no precise experimental data available. A typical range for D-value is 0 to 2 min. at around 121°C.
In other words, D-value is the time required in minutes to destroy the 90% population of the micro-organisms.
D-Value vs. Time
Let us understand the importance of D-value with an example where we want to reduce micro-organisms with moist heat sterilization.
- Initial no. of microbes = 100 i.e. 102
- Target reduction of microbes = 10-6
- Constant Temperature of sterilization process (T) = 121°C
The table below is an experimental data explaining how the D-value affects microbial reduction time:
| D-Value (min.) | Time Required for Microbial Reduction (min) | Initial No. of Micro-organisms | Final No. of Micro-organisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 4 | 100 | 10-6 |
| 1 | 8 | 100 | 10-6 |
| 2 | 16 | 100 | 10-6 |
This data means, at 121°C, the residual contamination of 10-6 is gained from the initial contamination of 102 in:
- 8 mins if D121=1,
- 4 mins if D121=0.5 and
- 16 mins if D121=2.
Another way to calculate the D-value is by using the following formula.
D = t / (log Co – log C)
where, t – exposure time in minutes
Co – initial number of micro-organisms
C – final number of micro-organisms
Please remember, the log values we’re discussing here are log10 and not loge.
European Pharmacopoeia [E 10.0, 5.5.1] have defined Sterility as Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) = 10-6.
Theoretically equivalent to SAL, United States Pharmacopoeia [USP 43, <1229>] have defined a must for sterility as Probability of Non-Sterile Unit (PNSU) = 10-6 i.e. the probability of identifying a non-sterile unit or micro-organism in a batch or lot.
In the above table, the SAL values are 100 and 10-6. Hence, the probability of identifying non-sterile microbe is one in 100 and one in a million, respectively.
What is z-Value (Temperature Coefficient)?
Practically speaking, the t
The z-value is used to correlate the heat resistance of the micro-organisms to the changing temperature.
z-value is the number of degrees the temperature is required to be increased which will cause a 10-fold variation in the D-value.
Definition of Z-Value
The z-value is considered as 10°C for the temperature range from 100 to 130°C for steam sterilization. Generally, bacteria that form spores have a z-value range of 10 to 15°C while the non-spore-forming ones have a range of 4 to 6°C.
Approximately D-value varies by 10 times for variation of 10°C. This doesn’t mean that D-value varies by 1 time for 1°C variation. The rationale for this is beyond the scope of this topic. To keep things simple, only note that “Variation in 1°C requires a variation of D-value by 25-30%”.
The effect of changing temperature decreases considerably upon:
1. Changing the sterilization method
2. Raising the system temperature
For example, for dry heat sterilization of around 200°C, the z-value is considered as 20°C instead of 10°C.
Even a small temperature incline will impact steam sterilization. At the same time, it may be insignificant in dry heat sterilization.
At 121.1°C, practically no microbe has precise D=1 minute and z=10°C but co-firing these two parameters to estimate the F0 value provides sufficient room for error.
The D-value is measured in minutes while the z-value is a temperature coefficient measured in °C.
Let us see, how the D-value and z-value help to reach a meaningful outcome for the sterilization effectiveness.
F0 Value (Equivalent Exposure Time)
F0 value is the equivalent exposure time at 121.1°C to that of the actual exposure time at a variable temperature calculated with a temperature coefficient of the destruction of 10°C.
F0 Value Definition

where,
Δt – the time interval between two temperature readings
T – the temperature at time t of the product under sterilization
z – temperature coefficient (assumed as 10°C)
The term next to Δt in equation (2) is called Lethality Rate. You can calculate it individually or by averaging complete sterile hold data, the result will be equivalent.
Testing F0 Value And Its Meaning
Consider sterilization hold time of 30 min. at constant 121.1°C.
Put this in equation (2),

Solving we get, F0 = 30 min. (This is an ideal condition for steam sterilization)
But what if the temperature is increased or decreased from 121.1°C (ideal condition)?
Let’s find out…
Example 1 (Below Ideal Condition)
Consider sterilization hold time of 30 minutes at constant 110°C instead of 121.1°C, in a similar manner as above,

Solving we get, F0=2.33 min.
Hence, 30 minutes of sterilization at 110°C is lethally equivalent to 2.33 min. of sterilization at 121.1°C. (Compare this sentence with the definition of F0 value for easy understanding)
The crux of the example is,
121.1°C → 30 min. (Expected condition)
110°C → 2.33 min. (Actual condition compared to the expected condition)
Compared to the expected condition, the effective sterilization cycle time was only 2.33 instead of 30 minutes because of the lowered temperature of 110°C.
Now, let us understand “how long will it take to complete the sterilization?” for this condition. Meaning, if we maintain temperature 110°C constantly, how much hold time is required to achieve an F0 value of 30 min.
By reverse calculation, we can do this.
Let’s fix the F0 value to 30 minutes. The unknown part then would be Δt (sterile hold time).
Data we have now is F0=30 minutes and Temperature T=110°C
Putting these values in equation (2),

Solving we get, Δt=386 min.
When the temperature of the system under sterilization is maintained at a constant 110°C, the time of 386 min. (i.e. Sterile Hold Time) would be required to achieve the lethal effect of 121.1°C at 30 min.
Example 2 (Above Ideal Condition)
Consider sterilization hold time of 30 minutes at constant 125°C instead of 121.1°C, in a similar manner as above,
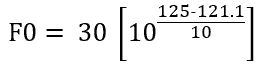
Solving we get, F0=73.64 min.
Hence, 30 minutes of sterilization at 125°C is lethally equivalent to 73.64 min. of sterilization at 121.1°C. (Compare this sentence with the definition of F0 value for easy understanding)
Simply put,
121.1°C → 30 min. (Expected condition)
125°C → 73.64 min. (Actual condition compared to the expected condition)
Compared to the expected condition, the effective sterilization cycle time was 73.64 instead of 30 minutes because of the elevated temperature of 125°C.
Let us understand “how long will it take to complete the sterilization?” for this condition. Meaning, if we maintain temperature 125°C constantly, how much hold time is required to achieve an F0 value of 30 minutes.
By reverse calculation, we can do this. Let’s fix the F0 value to 30 min. The unknown part then would be Δt.
Data we have now is F0=30 minutes and Temperature T=125°C
Putting these values in equation (2),

Solving we get, Δt = 12.24 min.
When the temperature of the system under sterilization is maintained at a constant 125°C, the time of 12.24 min (i.e. Sterile Hold Time) would be required to achieve the lethal effect of 121.1°C at 30 min.
You may use this F0 Value Calculator to explore the different steam sterilization scenarios.
Key Takeaways
F0 value provides lethal equivalence between expected and practical conditions. When noting down the values of lethal doses, D-value and z-value (if obtained) become very important to evaluate the precise F0 value.
Sterilization cycles can fail even if the sterile hold time is completed if the average temperature of the system is below 121.1°C. This is because residual microorganisms cannot be reduced completely.
When the average temperature of the system is above the set value of 121.1°C, the sterilization may be lethally equivalent even before the sterile hold time completes.
Note: This lethal equivalence has technical value only when the steam used for sterilization is Saturated. Otherwise, it is pointless. To know more, read out exact steam quality requirements.
F0 value calculation can be done either post sterilization or in real-time depending upon the chosen method.
The ‘post sterilization’ approach helps in analyzing and evaluating the lethal equivalence once the cycle has finished. While real-time calculation with a suitable controller help actually control the sterilization cycle till it achieves the preset F0 value.
Most of the pharmaceutical companies practicing steam sterilization rely on the calculation of F0 value for analysis purposes only. Though the logic-based controllers are capable of effectively driving the sterilization cycles based on the F0 value.
Experts recommend using the F0 value when the steam sterilization at 121°C for 15 min. is ineffective. In fact, Maria Luisa Bernuzzi, a technical center expert at Fedegari group explains this so simply…

Indeed factual! Further, she also explains the overkill approach as per EU regulations…

This means the steam sterilization cycle can be F0-based or time-based but the important thing is, whichever way you go, you should meet the required lethality.
If you want to read about the validation approach for steam sterilization or autoclave, you can read it here.
F0 Value: FAQs
What is f0 value?
F0 value is an equivalent exposure time at 121.1°C to that of the actual exposure time at a different temperature calculated with a temperature coefficient z-value of 10°C. Read more in the above article.
How do you calculate f0 value in autoclave?
To calculate the F0 value, average the temperature of each probe during the sterile hold and then average the different temperatures to get one single temperature. Use the formula shown in the above article to estimate the F0 value.
What is D value and Z value?
D-value is the time (t) required at a specified temperature (T) to reduce the microbial population from 100% to 10% (1 log reduction). z-value is the number of degrees the temperature required to increase, which will effect a 10-fold variation of D-value.
Now, turning it over to you.
How do you interpret the F0 value? Is it the same as this? Or maybe something else.
Either way, comment below.